Operating a successful food truck requires more than just great recipes and a prime location. One of the most critical components of any mobile food business is reliable refrigeration equipment. Proper refrigeration ensures food safety, maintains ingredient quality, and complies with health regulations. This comprehensive guide explores the types, selection criteria, maintenance, and innovations in food truck refrigeration systems.
Types of Food Truck Refrigeration Equipment
Food trucks utilize specialized refrigeration units designed to withstand movement, vibration, and limited space. The main types include:
1. Undercounter Refrigerators & Freezers
These are compact units built into the food truck's counter space, providing easy access to frequently used ingredients. They are ideal for storing dairy, meats, and prepped items within arm's reach of the cooking station.
Undercounter refrigeration maximizes space efficiency in a compact kitchen.
2. Reach-In Refrigerators & Freezers
Larger than undercounter models, reach-in units offer greater storage capacity with one or more doors. They are essential for trucks with high-volume operations or those needing to store bulk ingredients.
3. Refrigerated Prep Tables
These combination units provide a refrigerated base with a stainless steel top for food preparation. They are perfect for salads, sandwiches, and burgers, keeping ingredients cold while allowing for efficient workflow.

4. Portable Refrigerators & Freezers
Powered by DC (battery), AC (shore power), or dual-power sources, portable units offer flexibility for catering events or supplemental storage. Some are designed with rugged wheels for easy transport.
Key Selection Criteria for Refrigeration Equipment
Selecting the right equipment involves balancing several factors:
| Criterion | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Size & Capacity | Measure available space and calculate storage needs based on menu and volume. | High |
| Power Source | Options: Propane, DC (12V/24V battery), AC (110V generator/shore power), or hybrid. | Critical |
| Energy Efficiency | Look for well-insulated units and efficient compressors to conserve battery/generator power. | High |
| Durability & Build | Stainless steel exteriors, robust hinges, and vibration-resistant components are essential. | High |
| Temperature Consistency | Must maintain safe temps (below 40°F for fridge, 0°F for freezer) in varying climates. | Critical |
| Health Code Compliance | Equipment must be NSF/ETL-Sanitary certified for commercial food service. | Mandatory |
Power Systems and Energy Management
Power is the lifeline of food truck refrigeration. Most trucks use a combination of systems:
- Generator Power: Common for AC units; requires sufficient fuel and noise management.
- Battery Systems: Deep-cycle batteries with inverters for DC units; silent but need recharging.
- Shore Power: Plugging into external AC power at fixed locations or events.
- Propane Absorption Units: Good for freezers, quiet, but less efficient in very hot weather.
An efficient setup often includes a battery isolator to charge batteries while driving and a transfer switch to toggle between power sources.
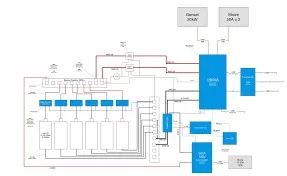
A typical multi-source power system for food truck refrigeration.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper Installation
Ensure adequate ventilation around condenser coils, secure mounting to prevent movement during transit, and proper sealing of door gaskets. Electrical connections must be performed by a qualified technician to prevent fire hazards.
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends equipment life and ensures food safety:
- Clean condenser coils monthly to prevent overheating.
- Check door gaskets for leaks and replace if worn.
- Monitor temperature daily with calibrated thermometers.
- Defrost manual freezers regularly to maintain efficiency.
- Inspect electrical connections and power cords for wear.
Innovations and Future Trends
The food truck industry is seeing advancements in refrigeration technology:
- Solar-Assisted Units: Integrating solar panels to reduce generator dependence.
- Smart Monitoring Systems: IoT sensors that alert owners via smartphone to temperature fluctuations or power failures.
- Variable-Speed Compressors: Adjust cooling output based on load, improving energy efficiency by up to 40%.
- Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Use of R-290 (propane) or CO2 systems with lower global warming potential.

Solar panels providing supplemental power for refrigeration units.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Initial investment for quality food truck refrigeration can range from $2,000 to $8,000 per unit. While costly, reliable equipment prevents food spoilage, avoids health code violations, and ensures customer satisfaction—delivering a strong return on investment. Consider both upfront cost and long-term operational expenses (power consumption, repairs).
Conclusion
Food truck refrigeration equipment is a vital investment that directly impacts food safety, operational flow, and business profitability. By carefully selecting the right type, power source, and size for your specific needs, and committing to regular maintenance, you can ensure your mobile kitchen runs smoothly and safely. As technology evolves, embracing energy-efficient and smart solutions will further enhance sustainability and control. Prioritize quality and compliance in your refrigeration choices to build a solid foundation for your food truck's success.