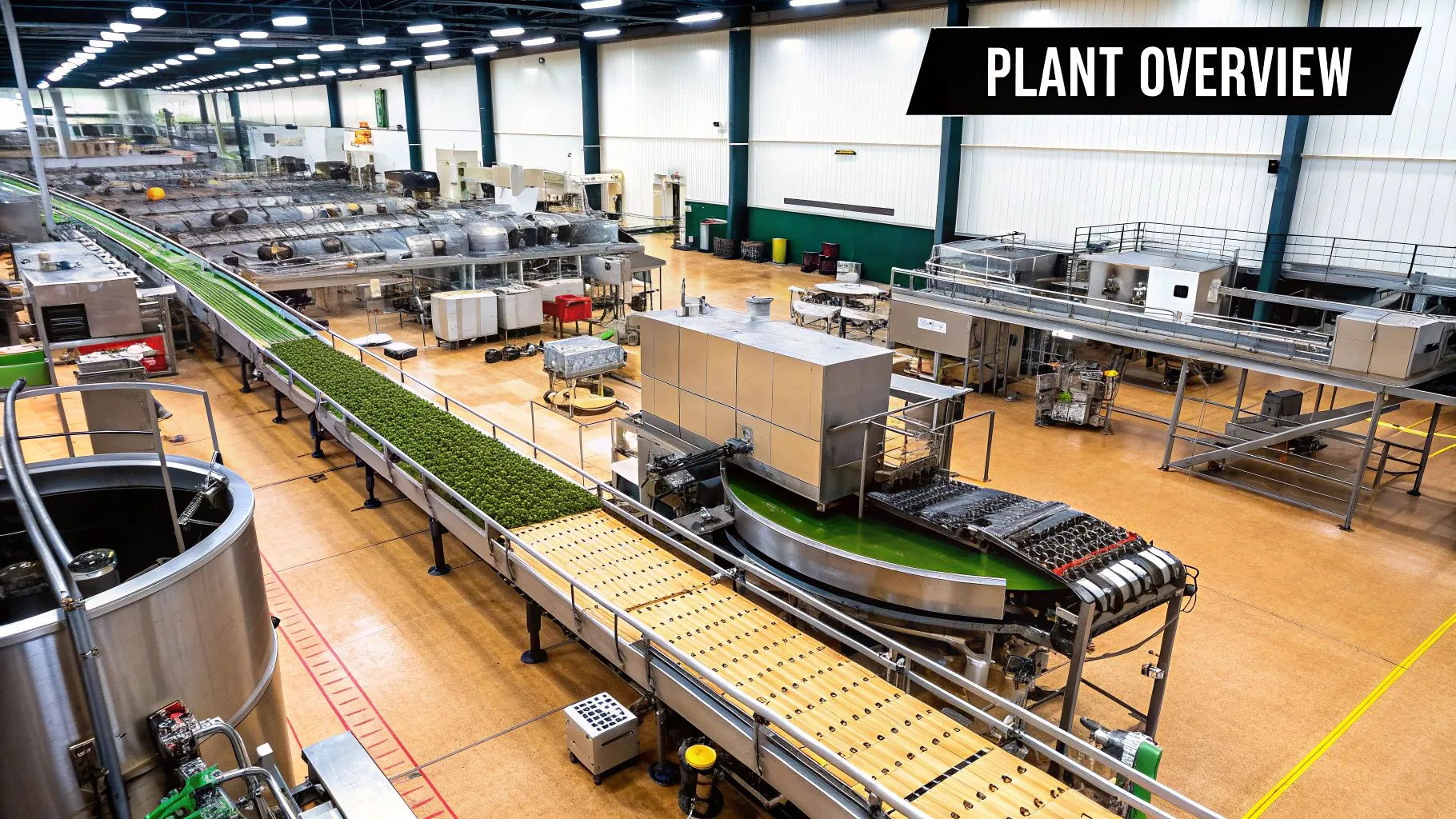
The global food processing industry is a complex, high-volume ecosystem where efficiency, safety, and consistency are paramount. At the heart of this system are food cutting equipment manufacturers, the specialized engineering firms that design and build the machinery responsible for slicing, dicing, shredding, and portioning raw ingredients into the precise forms required for further processing, packaging, and consumer sale. These manufacturers are not merely machine shops; they are innovation hubs that directly influence food safety standards, production scalability, product quality, and ultimately, the profitability of food producers worldwide.

Core Technologies and Product Innovations
Manufacturers continuously evolve their technologies to meet diverse industry demands. The core of their offerings revolves around several key machine types, each employing distinct cutting principles.
High-Speed Precision Slicers
These machines use ultra-sharp, rotating blades or reciprocating motions to produce consistent slices of meat, cheese, vegetables, and baked goods. Innovations include laser-guided thickness control and automatic self-sharpening systems.
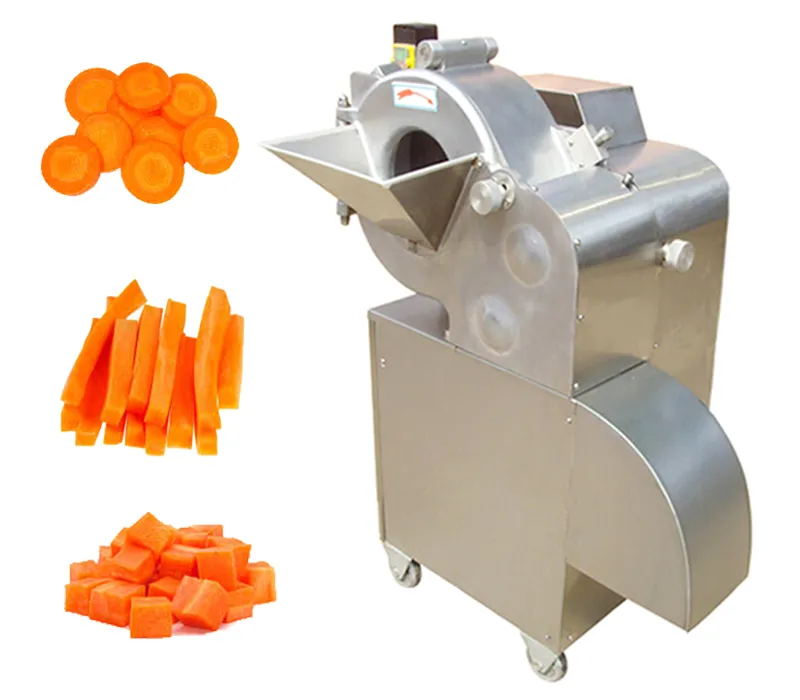
Dicing and Cubing Systems
Through a combination of initial slicing and subsequent cross-cutting actions, these systems transform products into perfect cubes or strips. They are essential for products like frozen potatoes, fruits for salads, and diced meats.

Guillotine and Band Saw Cutters
Primarily used in meat and poultry processing, these powerful machines handle frozen blocks, bone-in meat, and whole carcasses with strength and accuracy, minimizing waste.
Waterjet Cutting Technology
A non-thermal, sanitary method using ultra-high-pressure water, sometimes with abrasives, to cut delicate products like cakes, soft cheeses, and ready-to-eat meals without crushing or generating heat that affects quality.
Key Considerations for Food Processors When Selecting a Manufacturer
Choosing the right equipment partner is a strategic decision. The following table outlines the critical evaluation criteria:
| Criteria | Description | Impact on Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Hygienic Design & Materials | Use of stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316), CIP (Clean-in-Place) capabilities, smooth surfaces, and minimal crevices. | Reduces allergen cross-contamination risk, meets FDA/USDA/EU regulations, shortens cleaning downtime. |
| Cutting Precision & Yield | Ability to maintain consistent cut dimensions and minimize product loss as waste. | Directly affects product quality, portion control, and raw material cost efficiency. |
| Throughput Capacity & Uptime | Speed (kg/hour) and reliability under continuous operation, with easy maintenance access. | Determines production line capacity and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). |
| Flexibility & Changeover | Speed and tooling required to switch between different products or cut sizes. | Enables production of multiple SKUs on one line, crucial for batch producers. |
| Safety Features | Integrated safety interlocks, blade guards, emergency stops, and lock-out/tag-out compliance. | Protects operators, ensures compliance with occupational safety standards (e.g., OSHA). |
| Technical Support & Service | Availability of spare parts, field service engineers, training, and remote diagnostics. | Minimizes production losses from breakdowns and ensures long-term machine viability. |
Leading Market Segments and Applications
Food cutting equipment is ubiquitous across all protein, fruit, vegetable, and bakery processing lines.
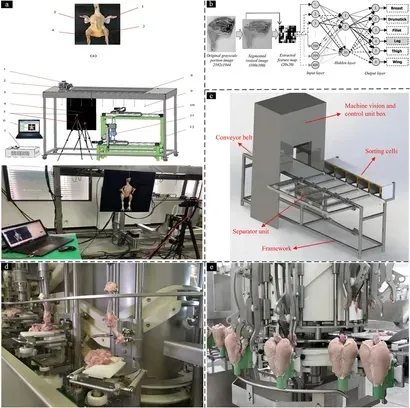
Meat & Poultry: This segment demands the most robust equipment for breaking, deboning, slicing, and trimming. Manufacturers here focus on durability, yield optimization software, and strict hygiene protocols.
Fruits & Vegetables: Equipment ranges from gentle peelers and corers to high-speed slicers for potato chips and julienne cutters for stir-fry mixes. Resistance to corrosion from acidic products is key.
Bakery & Confectionery: Precision band saws for frozen dough, gentle slicers for delicate cakes, and wire cutters for cookies are typical. Crumb management and precision are critical.
Cheese & Dairy: Block cutters, shredders, and slicers must handle products with varying textures and fat contents while maintaining strict sanitary standards.
Future Trends Shaping Manufacturing
Smart Industry 4.0 Integration
Modern machines are becoming data nodes on the factory network. IoT sensors monitor blade wear, motor load, and output quality in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and seamless integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems).
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Manufacturers are designing equipment to maximize yield from raw materials, directly reducing waste. Additionally, energy-efficient drives and designs that use less water for cleaning are becoming standard.
Advanced Automation and Robotics
Collaborative robots (cobots) are being integrated for loading/unloading or performing intricate cutting tasks alongside human workers, addressing labor shortages and enhancing safety.

Customization and Modular Design
To serve niche markets and specialized products, leading manufacturers offer highly customizable solutions and modular machines that can be reconfigured as production needs change.
Conclusion
Food cutting equipment manufacturers are indispensable partners in the food supply chain. Their relentless pursuit of innovation in precision engineering, hygienic design, and digital integration directly empowers food processors to meet the escalating demands for safety, efficiency, quality, and variety. As consumer trends and regulatory landscapes evolve, these manufacturers will continue to be at the forefront, developing the intelligent, sustainable, and adaptable cutting solutions that will shape the future of food production.